Implementation of high-speed, high-capacity communication functions in historic buildings, and construction of an optical fiber network in the Republic of Chile
- Using small-diameter optical fiber cables to transform historic school buildings into intelligent buildings -
Our company has built an optical fiber network at a university in the Republic of Chile, and held a handover ceremony for this project in March of this year. By installing optical fiber cables with world-leading technology, we were able to provide the historic buildings of a university with high-capacity, high-speed communication functions while preserving their architectural status.
Background
In the Republic of Chile, the construction of optical fiber networks is proceeding based on initiatives such as the “2013 - 2020 Digital Agenda for Chile” policy adopted in May 2013. Legislation requiring the installation within buildings of optical fiber cable systems sufficient for allowing subscribers to select their desired communication services was also put into effect in January 2015, leading to expectations for the accompanying promotion of FTTH(note 1) services.
There are many historic buildings still remaining in Chile, but the existing cable conduits in these buildings have no excess space and it is not possible to lay out new conduits, so the installation of new optical fiber cables for communications providers is at times a difficult task. In order to resolve this issue, optical fiber cables which could be installed as an addition even in confined spaces were required.
Content
Our company received an order to construct an optical fiber network for the Universidad Tecnica Federico Santa Maria (UTFSM) in the Republic of Chile, carried out as part of a project by Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, and we recently held the handover ceremony for this project.
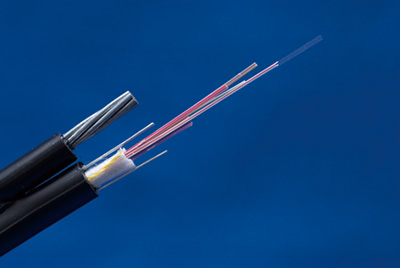
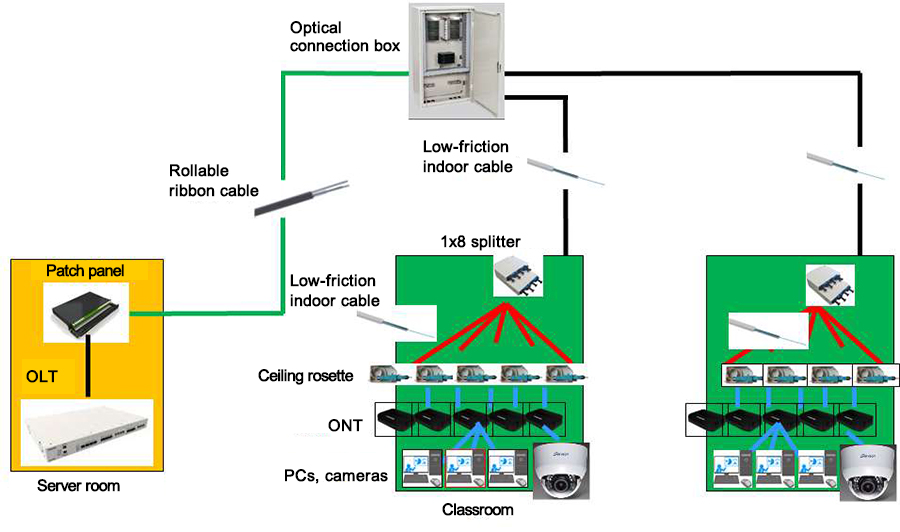
Established in 1929, UTFSM had been faced with the issue of installing new optical fiber cables in its historic school buildings. By using “low-friction indoor cables(note 2)” which are small-diameter optical indoor cables with reduced-friction coverings, we were able to install cables into narrow conduits. For the backbone systems on the premises of the university, we used “rollable ribbon cables”(note 3) which have excellent workability while being small in diameter and lightweight. This allowed us to preserve the condition of the historic buildings while transforming them into “intelligent buildings” with an optical fiber network of roughly 30 core km.
(note 1)FTTH: An acronym for “Fiber To The Home”. This refers to access telecommunications systems in which optical fiber is brought directly into subscribers’ homes and used as the transmission path, as well as the information and telecommunications services these systems provide.
(note 2)Low-friction indoor cables: Cables whose outer coverings use a material with a coefficient of friction reduced to roughly 1/5 that of conventional coverings, and whose cross-sectional area is roughly 1/2 as large. They are also made to have moderate rigidity so they can be passed through conduits more easily.
(note 3)Rollable ribbon cables: Cables which contain optical fiber ribbons consisting of multiple optical fibers arranged in a single row and bonded together at intervals. Since these ribbons allow the connection of multiple cores all at once, the time required for installation can be reduced. Furthermore, their ability to be easily deformed (rolled up) enables high-density packaging and allows the cables to have smaller diameters and lighter weights.
The handover ceremony was a grand event participated in by roughly 70 related parties, including Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications as well as the Vice-Minister of the Republic of Chile’s Subsecretaría de Telecomunicaciones, the President of UTFSM, communications providers such as Entel, and affiliated parties from nearby universities.
With the opportunities provided by this ceremony allowing us to secure other orders such as for a new FTTH pilot project at a nearby university, we will continue to make contributions to achieving high-speed, high-capacity communications across our world.
About Furukawa Electric Group
Furukawa Electric (TSE; 5801, ISIN; JP3827200001) Group started business in 1884, when its copper-smelting facility and wire manufacturing factory was established. Since then Furukawa Electric has become pioneers in the latest technologies by addressing diverse technological issues. Furukawa Electric has released products in a number of areas, including telecommunications, electronics, automobiles, and construction, with the three types of materials it works with at their core, namely, optics, plastics, and metals. Many of these products have attained the top global market share, and all of its products have contributed to society in numerous business areas. Furukawa Electric reported consolidated revenues of JPY 843.3 billion (approximately USD 7.8B) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017.







 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share