Furukawa Electric Develops Heat-resistant Low Insertion Force Cu-Sn Plating for Automobile Terminals
- Heat-resistant with lower insertion force makes material ideal for wire harness terminals -
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. has developed Heat-resistant Low Insertion Force Cu-Sn Plating that offers both heat resistance and low insertion force characteristics, as a contact material (terminal material) for small connector terminals found in automobile wire harnesses.
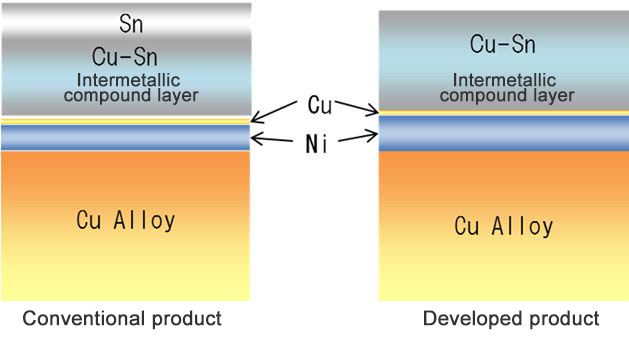
This plating forms an intermetallic compound layer(note 1) from copper (Cu) and tin (Sn) on the surface, that offers both low insertion force and fretting-resistance(note 2)—two qualities required by materials used for small connector terminals. Furukawa Electric plans to begin shipping samples this spring.
(note 1)Intermetallic compound:
A compound formed from two or more types of metals. It exhibits different properties from those of single metals. Two types of intermetallic compounds formed from copper and tin are generally known. These compounds offer a variety of properties, such as being harder than tin alone.
(note 2)Fretting:
A phenomenon where automobile vibrations create extremely small vibrations in terminal contacts, shaving the tin plating layer down and creating abrasion powder. Oxidation of this abrasion powder causes contact defects between contacts.
Background
Following recent increases in the amount of electronics and wires mounted in automobiles, the connector terminals in automobile wire harnesses continue to undergo multipolarization and grow smaller (thinner). The insertion force per terminal is tending to increase, causing workability during vehicle assembly to suffer.
There are also an increasing number of cases where terminals are used in high-temperature environments (such as near engine compartments) due to mounting space considerations. There is therefore a demand for connector terminal plating material that supports multipolarization, offers low insertion force, and offers connection reliability in high-temperature environments.
Content
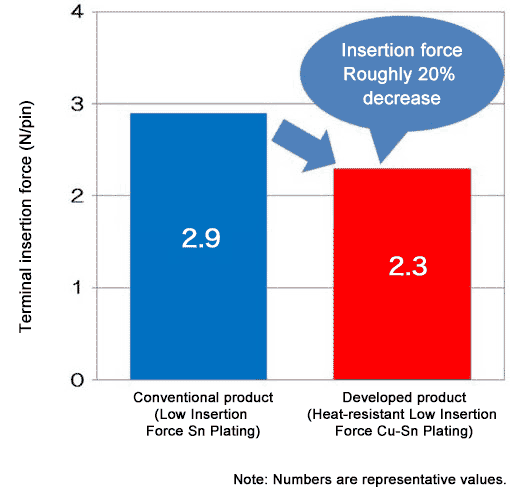
Furukawa Electric has developed Heat-resistant Low Insertion Force Cu-Sn Plating that offers low insertion force and the same low contact resistance as conventional products. This plating forms an intermetallic compound layer from copper and tin, that results in an insertion force that is roughly 20% lower than that of conventional low insertion force tin plating, and a surface intermetallic compound layer that is resistant to being shaved off. It therefore helps to curb contact resistance from increasing due to fretting.
In addition to small terminals that are susceptible to fretting, this plating is capable of reducing insertion force for large connectors that require auxiliary mechanisms for insertion, making it ideal as a connector terminal material for automobile wire harnesses.

Comparison with Conventional Product
About Furukawa Electric Group
Furukawa Electric (TSE; 5801, ISIN; JP3827200001) Group started business in 1884, when its copper-smelting facility and wire manufacturing factory was established. Since then Furukawa Electric has become pioneers in the latest technologies by addressing diverse technological issues. Furukawa Electric has released products in a number of areas, including telecommunications, electronics, automobiles, and construction, with the three types of materials it works with at their core, namely, optics, plastics, and metals. Many of these products have attained the top global market share, and all of its products have contributed to society in numerous business areas. Furukawa Electric reported consolidated revenues of JPY 874.9 billion (approximately USD 8.0B) for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2016.







 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share