Through cellular foaming of engineering plastic and super engineering plastic, achieved lightweight × low dielectric
Smart Cellular Board™ (hereinafter “SCB™”) is a cellular foamed, board type low dielectric material. Using our original foaming technology, it is possible to foam highly heat resistant plastics such as engineering plastic and super engineering plastic and obtain even lower dielectric properties than are achievable with typical low dielectric plastics.
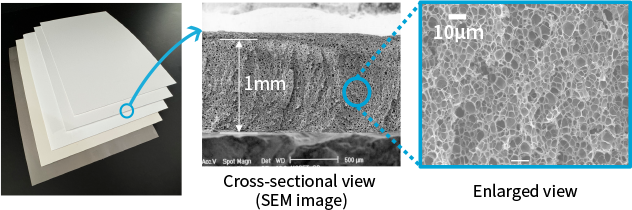
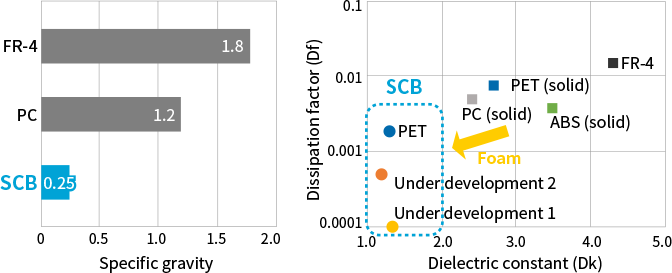
SCB™ realizes lightweight, low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor.
As a material with low dielectric constant (Dk) and low dissipation factor (Df), when SCB™ is used as the material for circuit boards and radomes, it can solve issues including increased transmission loss and reduced radio wave permeability arising due to the use of higher frequencies within the telecommunications market as it shifts to 5G and 6G.
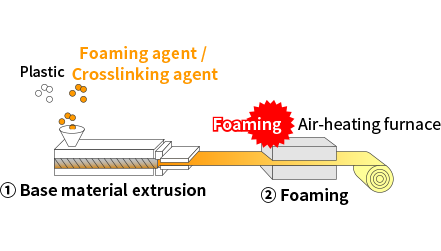
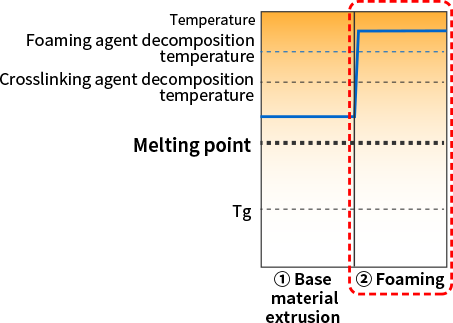
Original technology used for SCB™
With our original batch foaming technology, which enables foaming below the melting point, it is possible to foam plastics with a high melting point (engineering plastic and super engineering plastic)!
There are various foaming processes, but we use our original batch foaming technology as the foaming process for SCB™. Through differences in the manufacturing process as described next, we are able to realize foaming below the melting point when the material is still in solid form.

Chemical foaming
Cannot foam plastics with a melting point higher than the decomposition temperature of the foaming/ crosslinking agent
Difficult to foam engineering plastic and super engineering plastic with a high melting point
Batch foaming

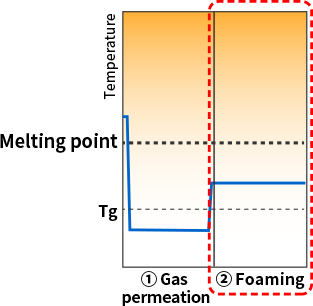
Because gas permeation is done at room temperature and foaming is done below the melting point, it is possible to foam plastics with a high melting point
Possible to foam engineering plastic and super engineering plastic with a high melting point
Specification
| Item | Units | SCB™-B1 | SCB™-Z1 | SCB™-Under development 1 | SCB™-Under development 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base plastic | PET | PP | - | - | |
| Density | g/cm3 | 0.23 | 0.33 | 0.29 | 0.18 |
| Melting point | ℃ | 260 | 165 | - | 278 |
| Tg | ℃ | 75 | - | 165 | 90 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | ppm/℃ | 43 (-40~60℃) |
- | 60 (23℃~60℃) |
50 (-20~100℃) |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 15.2 | MD:12.2 TD:5.9 |
16.4 | 7 |
| Tensile elongation | % | 70 | MD:62 TD:90 |
7.5 | 50 |
| Degree of crystallinity | % | 36.1 | - | 0 | 20 |
| Dielectric characteristics | Dielectric constant (Dk) | 1.3 | 1.36 | 1.35 | 1.2 |
| Dissipation factor (Df) | 0.002 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0005 | |
| Thickness | mm | 1.0 | 5.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Width | mm | 750 | 1350 | - | - |
| Length | mm | 1300 | 2000 | - | - |
-
(Note)
Figures are representative values and are not standard values.
-
(Note)
Dimensions are one example. Please inquire about other sizes.
Proposals
-
Applications
 Proposal for a radome material
Proposal for a radome material- Low dielectric constant (Dk)
- Low dissipation factor (Df)
- High radio wave permeability
- Lightweight
- Plastic material that is simple to design (limit the frequency/ thickness dependency)
-
Applications
 Proposal for a circuit board material
Proposal for a circuit board material- Low dielectric constant (Dk)
- Low dissipation factor (Df)
- Reduced transmission loss
- Limited heat generation
- Formability for printed circuit boards
-
Characteristics
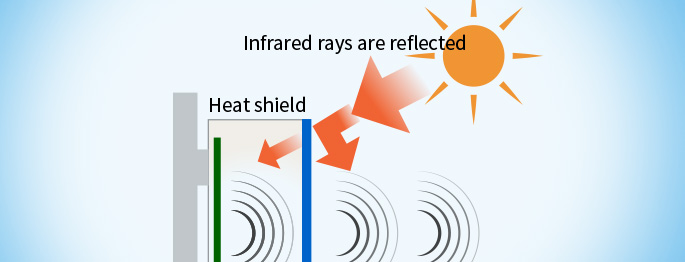 Proposal of infrared ray reflective characteristics for reflecting solar heat
Proposal of infrared ray reflective characteristics for reflecting solar heat- Reflects infrared rays
- Limited radiant heat
“Smart Cellular Board” and “SCB” are registered Japanese trademarks of Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
Our SCB™ can solve the issues often faced when designing base stations that use high frequency radio waves in 5G/ Beyond 5G/ 6G telecommunications.

