Furukawa Electric and Nichia Form a Business Alliance in Core Technology (Laser Processing) Supporting the Production of Mobility Electrification
- Deepening market exploration and co-creation by integrating production bases for blue laser diode modules and opening joint operation labs for laser processing -
- Agreement on a long-term business alliance aimed at making blue lasers the de facto standard for copper processing in xEV core components
- Integration of production bases for blue laser diode modules (LDM) for processing, promotion of the joint development of next-generation blue LDMs, and opening of a jointly managed application laboratory
- Contributing to the promotion of the spread of xEV throughout society and the realization of a sustainable society
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (Head office: 2-3, Marunouchi 2-chome, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Keiichi Kobayashi; hereafter, “Furukawa Electric”) and Nichia Corporation (Head Office: 491 Oka, Kaminaka-cho, Anan City, Tokushima Prefecture; President: Hiroyoshi Ogawa; hereafter, “Nichia”) have agreed to a long-term business alliance aimed at strengthening a sustainable collaborative relationship in core technologies (laser processing) that will support the promotion of the electrification of mobilities.
The electrification (xEV) of mobilities as a means of realizing a decarbonized society, is accelerating and we are entering a period of great change. Because copper is widely used in motors, batteries, and core components of xEV, efficient laser processing of copper has become a major challenge in the improvement of productivity. Based on the 2017 agreement to build an equal and good relationship that will span a long period, Nichia and Furukawa Electric jointly developed a blue LDM, and by combining it with an infrared laser for optimization, realized stability, speed and quality in processing not seen with existing or other technologies, thereby establishing processing technology with a hybrid laser (note 1) that contributes to the resolution of issues in copper laser processing.
The agreement on this business alliance aims to allow the further evolution of the processing performance of blue-IR hybrid lasers, the core technology that will support xEV, by strengthening the technological integration of both Nichia and Furukawa Electric, and making blue-IR hybrid lasers the de facto standard in copper processing.
We will contribute to the improvement of xEV core component production efficiency and cost reductions, the spread throughout the society of xEV and the realization of a sustainable society.
The agreement on this business alliance confirms and expresses the results of combining the technologies Nichia and Furukawa Electric have cultivated to this point and repeated co-creation, and is the first step towards the further strengthening and development of their mutually cooperative relationship from now on. Nichia and Furukawa Electric will advance the integration of production bases for blue LDMs for processing and the joint development of next-generation blue LDMs while also looking ahead to the establishment of a joint venture company in the future. In addition, as part of our activities to explore the market and propose solutions for copper laser processing to customers jointly, Nichia and Furukawa Electric will promote the establishment of a jointly-managed application laboratory for blue-IR hybrid laser processing at Nichia’s Yokohama Research Center.
By promoting these concrete co-creation efforts, Nichia and Furukawa Electric aim to allow the further evolution of the processing performance of blue-IR hybrid lasers, a core technology that supports xEV, and provide processing solutions, thereby contributing to the improvement of customers’ copper laser processing productivity.
Background
The development of xEV, which is effective against climate change as no NOx (nitrogen oxide), PM or CO2 is emitted while driving, has been promoted around the world in recent years aimed at the realization of a sustainable society. Most recently, momentum to abolish gasoline vehicles by the 2030s has risen rapidly under the policies of various governments. In such circumstances, it is apparent that the manufacturing volumes of parts such as the batteries, motors and inverters essential to xEV will grow dramatically.
Various welding methods including resistance, ultrasonic and arc weldings are being used to join copper parts as a conductor, at plants that manufacture batteries, motors, inverters, and other core xEV components (Fig. 1). The introduction of laser welding using a fiber laser, with stable output through its continuous waves, and a semiconductor laser as the processing heat source is now considered with the aim of further improving efficiency, including the reduction of CO2 emitted from plants and process automation. Against this background, there is a growing need to replace the conventional laser light source using near-infrared light (1070 nm wavelength band), which has extremely high optical reflectivity with copper, making high-quality processing difficult, with a high-power blue laser (450 nm wavelength band), which has good optical absorption with copper.
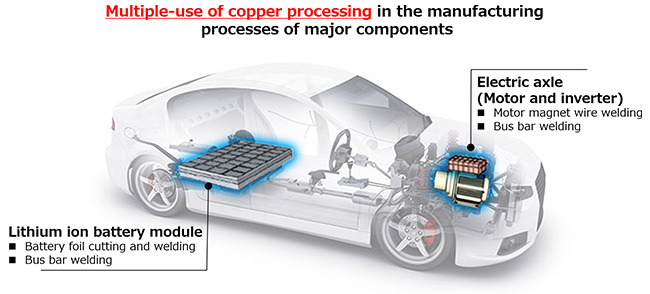
Details
Integration of blue LDM production sites
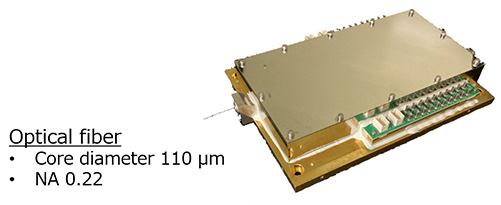
Since October 2017, Nichia has developed a high-power blue laser diode and Furukawa Electric has developed a blue LDM, and in January 2021, Nichia and Furukawa Electric jointly developed a blue LDM with an optical output of 170 W (Fig. 2).
To accelerate the development of blue LDM products from now on, Nichia and Furukawa Electric will integrate their blue LDM plants at the Nichia business site in Tokushima Prefecture from May 2022 and aim for the further deepening of the joint development framework and the combined achievement of higher output, higher brightness, higher reliability and price competitiveness for blue LDMs. Nichia and Furukawa Electric are also considering the establishment of a joint venture for the production of blue LDMs in the future.
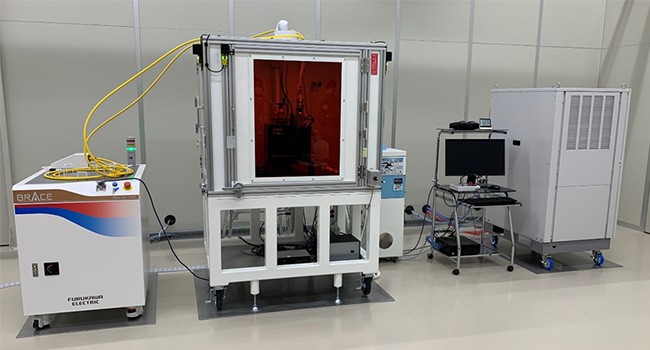
Opening of joint application laboratory
In co-creation in laser processing technology, Nichia and Furukawa Electric will open a dedicated application laboratory at Nichia’s Yokohama Research Center in June 2021 and will introduce Furukawa Electric’s BRACE™-I hybrid laser (Figure 3, (note 2)).
Nichia and Furukawa Electric will propose laser processing solutions jointly while performing test processing using samples brought in by customers at this lab. As the first application, Nichia and Furukawa Electric will use their knowledge of manufacturing the components essential for xEV to provide mainly the welding processing of the copper foil current collectors and bus bars used in lithium-ion batteries, and will promote exploration of the laser processing market based on marketing activities conducted through joint management of this laboratory.
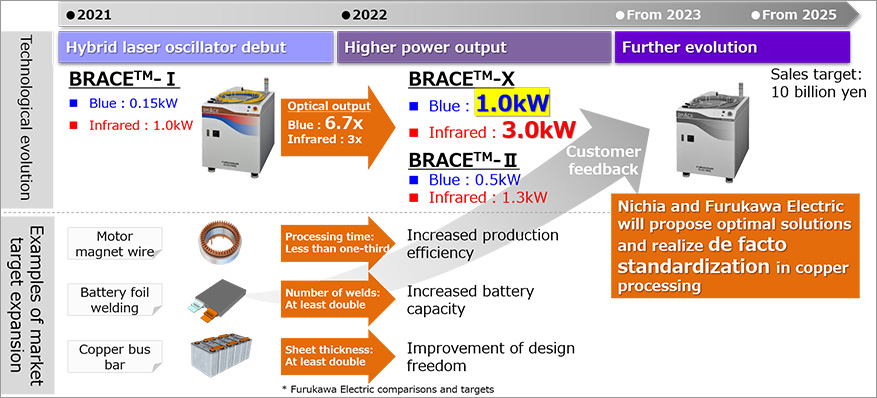
Product roadmap for the BRACE™ next-generation hybrid laser
Furukawa Electric released the BRACE™-I, a blue-IR hybrid laser equipped with a blue LDM developed in conjunction with Nichia last January. In fiscal 2022, Nichia and Furukawa Electric will aim for the commercialization of the next-generation hybrid lasers BRACE™-II and BRACE™-X, which will be essential for the new laser processing that will promote the spread of xEV (Fig. 4). Nichia and Furukawa Electric will increase the presence of BRACE™ by realizing laser processing of copper at the highest level in the world, and will capture market needs accurately to continue to provide high-quality, fast and reliable laser processing solutions.
(note 1)Hybrid laser: A laser oscillator that combines a blue laser oscillator and an infrared fiber laser oscillator.
(note 2)BRACE™: Trademark of Furukawa Electric (pending). The “BR” stands for blue and infrared, and “ACE” means “the best.” As the single word “BRACE,” the name has the meaning “pair” or “combination.”
Related news release
Furukawa Electric Group’s efforts towards the SDGs
Based on the “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” adopted by the United Nations, the Furukawa Electric Group has formulated the “Furukawa Electric Group Vision 2030” which sets the year 2030 as its target and is advancing efforts with the aim to “Build a sustainable world and make people’s life safe, peaceful and rewarding, Furukawa Electric Group will create solutions for the new generation of global infrastructure combining information, energy and mobility.” Toward the achievement of our Vision 2030, we will take open, agile, and innovative approaches to promote ESG management that that aims to increase corporate value over the medium to long term and will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs.








 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share