Reduce of Raman Amplifier Power Consumption with New Dual Port Raman Pump
- Advancing Power Efficiency in Optical Networks -
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (Head Office: 2-6-4 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Hideya Moridaira) has successfully reduced power consumption in Raman amplifiers with its newly developed Dual Port Raman Pump Laser (DPRP). This high-output, low-power solution cuts energy use by 32-39% compared to existing products, enhancing efficiency in optical communication networks.
Furukawa Electric will showcase the DPRP at OFC 2025 in San Francisco, California, from April 1-3, 2025, at the Lightera Booth No. 2843.
Background
Addressing Growing Data Demands
As data traffic surges due to AI, machine learning, and high-speed communication, network infrastructure must support longer transmission distances without compromising signal quality. Raman amplifiers play a crucial role by strengthening optical signals while preserving integrity.
With increasing demand for high-speed transmission, amplifiers must now support wider bandwidths across the S-, C-, and L-bands. This expansion requires more pump lasers, making energy-efficient, high-output solutions essential.
Details
Innovative DPRP Technology
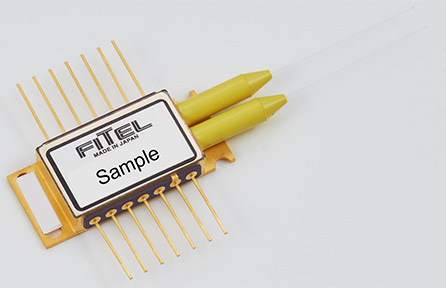
Furukawa Electric’s Dual Port Raman Pump Laser (DPRP) integrates two laser chips into a single package, reducing the total number of required pump lasers while improving efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Lower Power Consumption – Reduces total energy use by leveraging efficient cooling mechanisms.
- Optimized Heat Management – Minimizes thermal load for better Thermoelectric Cooler (TEC) performance.
- Compact & High-Performance Design – Uses high accuracy fiber coupling technology and Indium Phosphide (InP(note 1)) semiconductor laser chip structure for low-loss, high-efficiency.
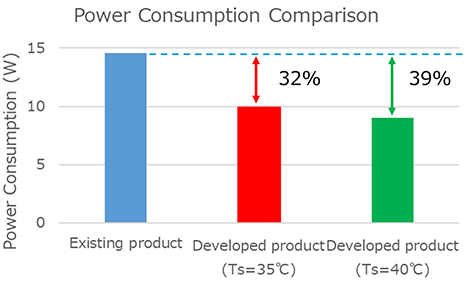
Power Efficiency Comparison
Furukawa Electric’s Dual Port Raman Pump Laser (DPRP) integrates two laser chips into a single package, reducing the total number of required pump lasers while improving efficiency. Key benefits include:
| Configuration | Power Consumption | Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| 2 Single-Port Lasers (0.5W x 2) | 14.6W | - |
| 1 DPRP (0.5W x 2) @ Ts=35°C | 9.9W | -32% |
| 1 DPRP (0.5W x 2) @ Ts=40°C | 9.0W | -39% |
Furukawa Electric’s DPRP technology builds on 25 years of fiber coupling and semiconductor expertise, delivering high-efficiency Raman amplification (patented, (note 2)) for next-generation optical networks.
Market Availability & Future Development
- Samples began shipping in November 2024.
- Showcased at OFC 2025 in San Francisco.
- Continued development of next-generation low-power laser technologies to further enhance energy efficiency.
(note 1)InP (Indium Phosphide): A III-V compound semiconductor that is used for the manufacture of laser diode chips and high-speed transistors
(note 2)US patent US 9,083,150 B2
The current development was conducted and achieved as part of the National Institute of Information and Communications Technology (NICT) commissioned research “Beyond 5G – Development of extended range optical node technology for realizing ultra-high speed, large volume networks” (Key Issue JPJ012368C04501) and the 2024 Function Realization and International Joint R&D Program “Innovative ICT Fund Projects for Beyond 5G/6G” (JPJ012368G60101).
Related News Release
Achieved 800mW Output with a Pump Laser for C-band Raman Amplifiers
Improved the performance of the dual port pump laser for Raman amplifiers
Furukawa Electric Group’s efforts towards the SDGs
Based on the “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” adopted by the United Nations, Furukawa Electric Group has formulated the “Furukawa Electric Group Vision 2030” which sets the year 2030 as its target and is advancing efforts with the aim to “Build a sustainable world and make people’s life safe, peaceful and rewarding, Furukawa Electric Group will create solutions for the new generation of global infrastructure combining information, energy and mobility.” Toward the achievement of our Vision 2030, we will take open, agile, and innovative approaches to promote ESG management that aims to increase corporate value over the medium to long term and will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs.







 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share