Development of the radome housing for next-generation telecommunications devices using the low dielectric material “Smart Cellular Board®”
- With the ability to customize for each installation environment, can realize performance requirements difficult to achieve with a single material -
- Developed the radome housing for next-generation telecommunications devices using SCB®, a low dielectric material that reduces dielectric constant and dissipation factor
- Possible to design customized housings to suit the installation environment using each grade within SCB® series that possess various characteristics
- Through the use of a layered structure, the characteristics of each grade complement each other to satisfy performance requirements that are difficult to achieve with a single material
Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd. (Head office: 2-6-2 Otemachi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo; President: Hideya Moridaira) developed a radome housing for next-generation telecommunications devices using the low dielectric material “Smart Cellular Board® (hereinafter SCB®)” that reduces dielectric constant and dissipation factor.
Background
As momentum accelerates toward the realization of smart cities and smart factories that connect various facilities and equipment through a network, the use of telecommunications devices is increasing and their installation locations are becoming more diverse. Moreover, depending on the device application, the frequency bands used are also becoming more diverse. For example, millimeter waves are used in automobile radar and to detect falls in medical facilities. Following these changes, the design of the radome housing, which acts as a cover to protect the next-generation telecommunications devices from the weather and sunlight, needs to be rigid, lightweight, heat resistant and water resistant in accordance with radio wave control matched to the frequency band and installation environment of each device, and it is becoming increasingly difficult to design these radomes.
Details
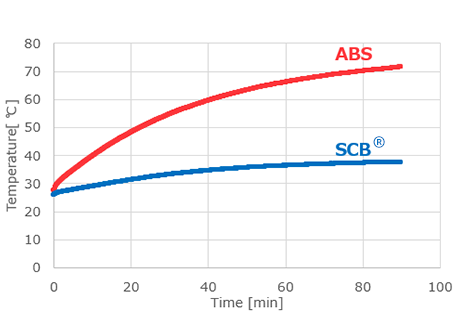
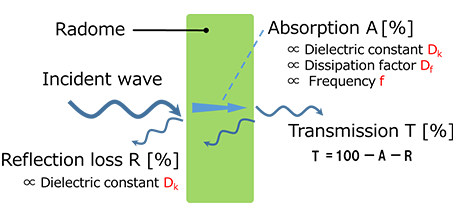
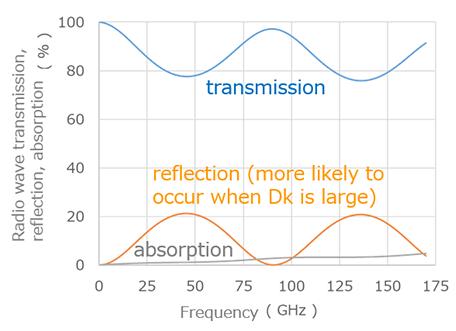
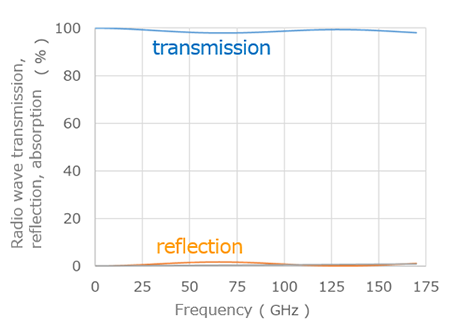
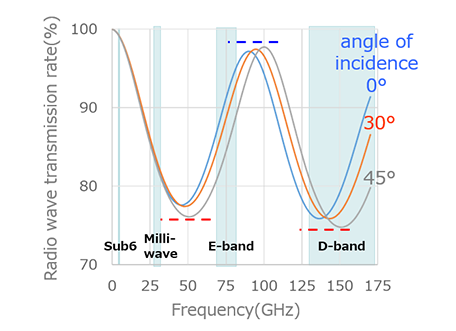
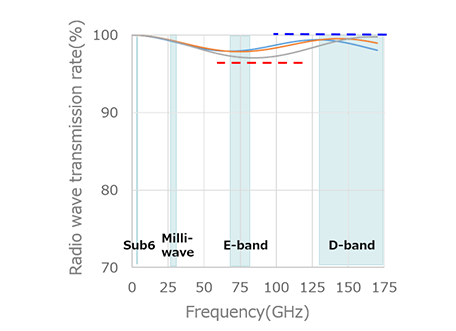
Furukawa Electric has developed a radome housing for next-generation telecommunications devices using SCB®, a low dielectric material that reduces dielectric constant and dissipation factor. It is possible to design a customized radome housing to match the installation environment through the use of different grades within the SCB® series that each possess various characteristics such as strength, water resistance and heat resistance. The different grades assembled into a layered structure complement each other to satisfy performance requirements that are difficult to achieve with a single material alone. For example, when installing the radome housing outdoors or for communications in the high frequency wavebands, heat accumulation inside the housing due to IR radiant heat and power consumption of the antenna circuit board is a problem. ABS plastic traditionally used for housings has excellent strength and heat resistance, but it is particularly susceptible to the effects of heat from IR radiation. However, the SCB® series has a grade with high reflectivity in the IR range, and by incorporating this grade on the outside of the housing, it acts as a heat shield and reduces the impact of radiant heating (Fig. 2).
Leveraging our unique SCB® technology, we will continue to develop materials that respond to customer requirements, and contribute to realizing a Beyond 5G/6G society.
“Smart Cellular Board” and “SCB” are registered Japanese trademarks of Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd.
Product homepage
Related news release
Furukawa Electric Group’s efforts towards the SDGs
Based on the “Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)” adopted by the United Nations, Furukawa Electric Group has formulated the “Furukawa Electric Group Vision 2030” which sets the year 2030 as its target and is advancing efforts with the aim to “Build a sustainable world and make people’s life safe, peaceful and rewarding, Furukawa Electric Group will create solutions for the new generation of global infrastructure combining information, energy and mobility.” Toward the achievement of our Vision 2030, we will take open, agile, and innovative approaches to promote ESG management that aims to increase corporate value over the medium to long term and will contribute to the achievement of the SDGs.








 Share
Share Tweet
Tweet Share
Share