Furukawa Electric Group’s financial results and financial situation are affected by the economic conditions in the various markets in which the Group sells its products and provides services. The important risks that have the potential to affect the Group’s financial results and financial situation are listed, as shown below. Risk items are defined as those with a medium or higher likelihood of occurrence and magnitude of impact, and, based on how the risks are perceived, they have been broadly categorized into “Management perspective risks” and “Operational perspective risks.” When implementing responses to each risk, particularly for the management perspective risks, rather than being independent risks, they are recognized to be mutually related. The forward-looking statements contained in the descriptions below are based on the Group’s estimates and assumptions made as of March 31, 2024.
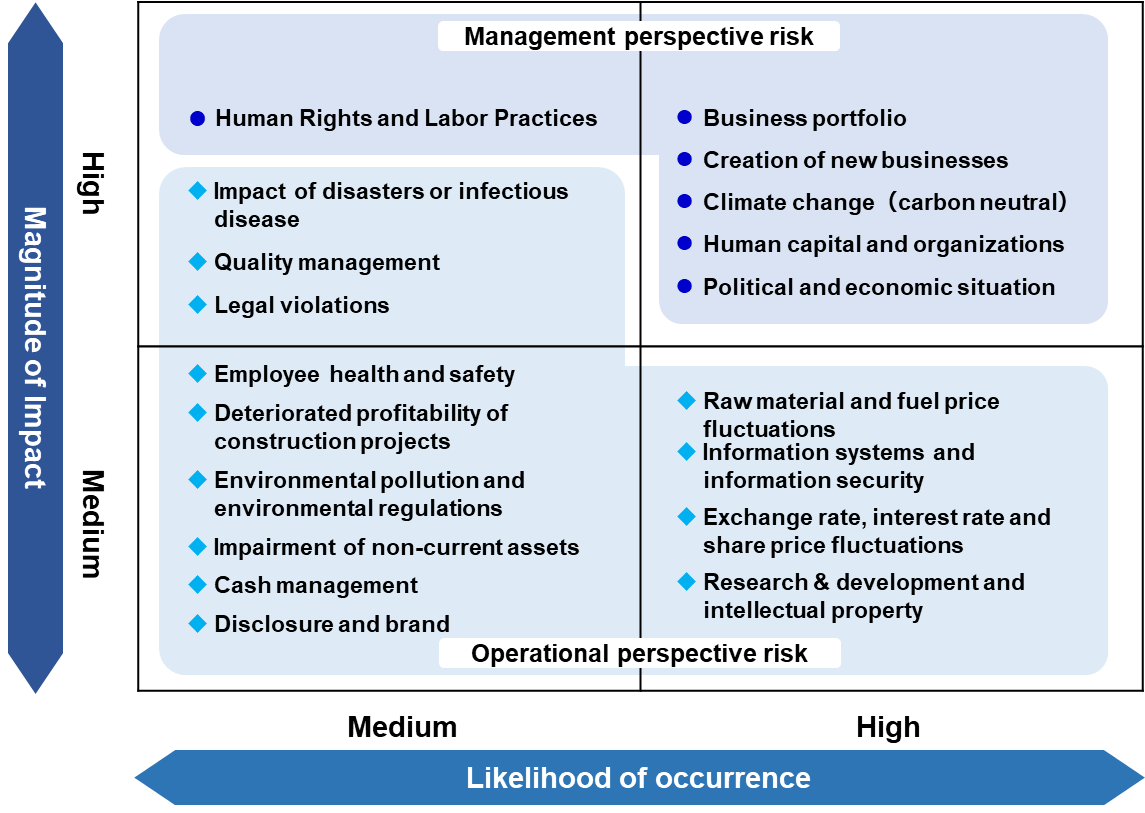
Management perspective risks
Business portfolio
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Creation of new businesses
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Climate change (carbon neutral)
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Human capital and organizations
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Political and economic situation
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Human Rights and Labor Practices
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Operational perspective risks
Impact of disasters or infectious disease
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Quality management
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Legal violations(Note)
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
High |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
(Note) We have been under investigation by the Brazilian competition law authorities concerning auto-parts cartel. In addition, the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries are the defendant in a series of class actions that seek compensation for damages caused by the auto-parts cartel in the United States. It may also be possible that the Company and its associates pay compensation for civil damages to their customers including automobile manufacturers. However, the Company has reached settlement with some plaintiff and customers concerning the above-mentioned on-going cases, and thus believes that it will have limited monetary impact on its financial results. We will continue to work with our corporate lawyers to resolve the issue early and minimize losses. Note that above on-going cases are all related to past violations of competition law including auto-parts cartel, and there are no such violation committed at this point in time.
Raw material and fuel price fluctuations
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Information systems and information security
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Exchange rate, interest rate and share price fluctuations
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Research & development and Intellectual property
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
High |
Employee health and safety
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Deteriorated profitability of construction projects
| Details of the risk |
(Domestic and overseas)
(Overseas) |
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Environmental pollution and environmental regulations
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Impairment of non-current assets
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Cash management
| Details of the risk |
(Funds procurement)
(Credit management) |
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |
Disclosure and brand
| Details of the risk |
|
|---|---|
| Main responses |
|
| Magnitude of impact |
Med. |
| Likelihood of occurrence |
Med. |






